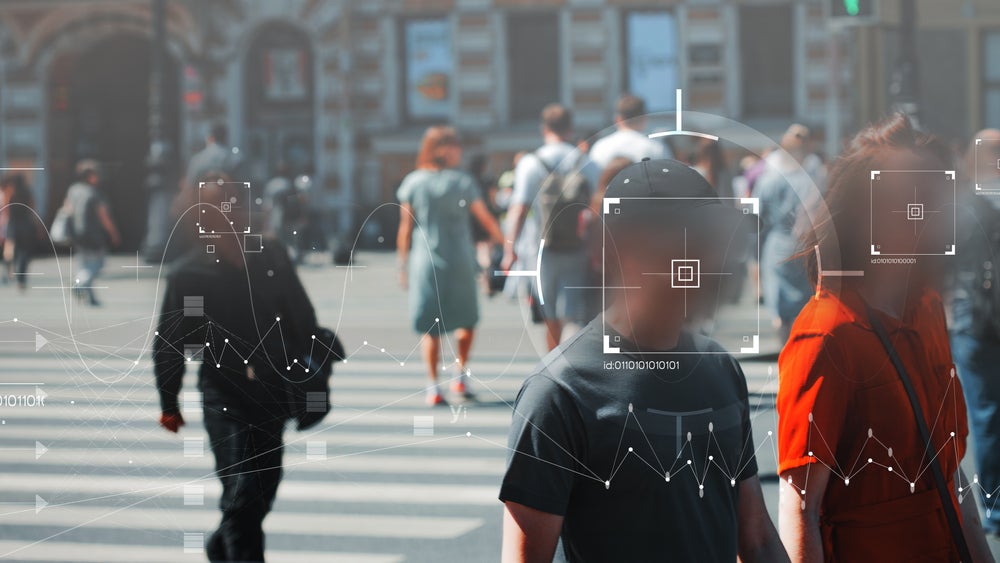
On December 6, 2024, London’s Metropolitan Police announced that it had made more than 500 arrests in the UK capital using facial recognition technology (FRT).
FRT has changed the way law enforcement agencies operate. By analysing facial features in real-time video footage, FRT can rapidly identify individuals, aiding in criminal investigations, missing person cases, and public safety initiatives.
How FRT works
FRT systems function by capturing images of individuals in public spaces and comparing them against a database of known offenders or people of interest. If a match is found, an alert is triggered, allowing law enforcement to intervene. The technology’s accuracy has significantly improved over the years, making it a reliable tool for identification.
FRT can quickly identify individuals who may be involved in criminal activity, enabling swift apprehension. This is particularly useful in cases where suspects are fleeing the scene or are unknown to officers. It can also locate missing persons, especially in cases where there are few clues or leads. By scanning public spaces and comparing images to missing person databases, law enforcement can quickly identify and locate individuals.
The tech can also be used in the case of public safety at large events, such as concerts and sporting events, to identify potential threats and prevent crime. It can also be used to monitor public spaces for suspicious behaviour, enhancing overall safety.
Risks and concerns
While FRT offers significant benefits, it also raises ethical concerns and privacy issues. Some key considerations include accuracy, bias, and privacy concerns. FRT systems are not infallible and can produce false positives or negatives. It is crucial to ensure that the technology is accurate and reliable to avoid wrongful arrests or misidentifications. There are concerns that FRT systems may be biased against certain groups, particularly minorities. It is essential to develop algorithms that are fair and unbiased to prevent discrimination.
The widespread use of FRT also raises privacy concerns. Constant surveillance of individuals, even in public spaces, can erode civil liberties. It is important to balance the need for public safety with individual privacy rights. As FRT technology continues to advance, it is likely to play an even greater role in law enforcement. However, it is crucial to address the ethical and privacy concerns associated with its use. By striking a balance between innovation and individual rights, we can harness the power of FRT to improve public safety while safeguarding civil liberties.