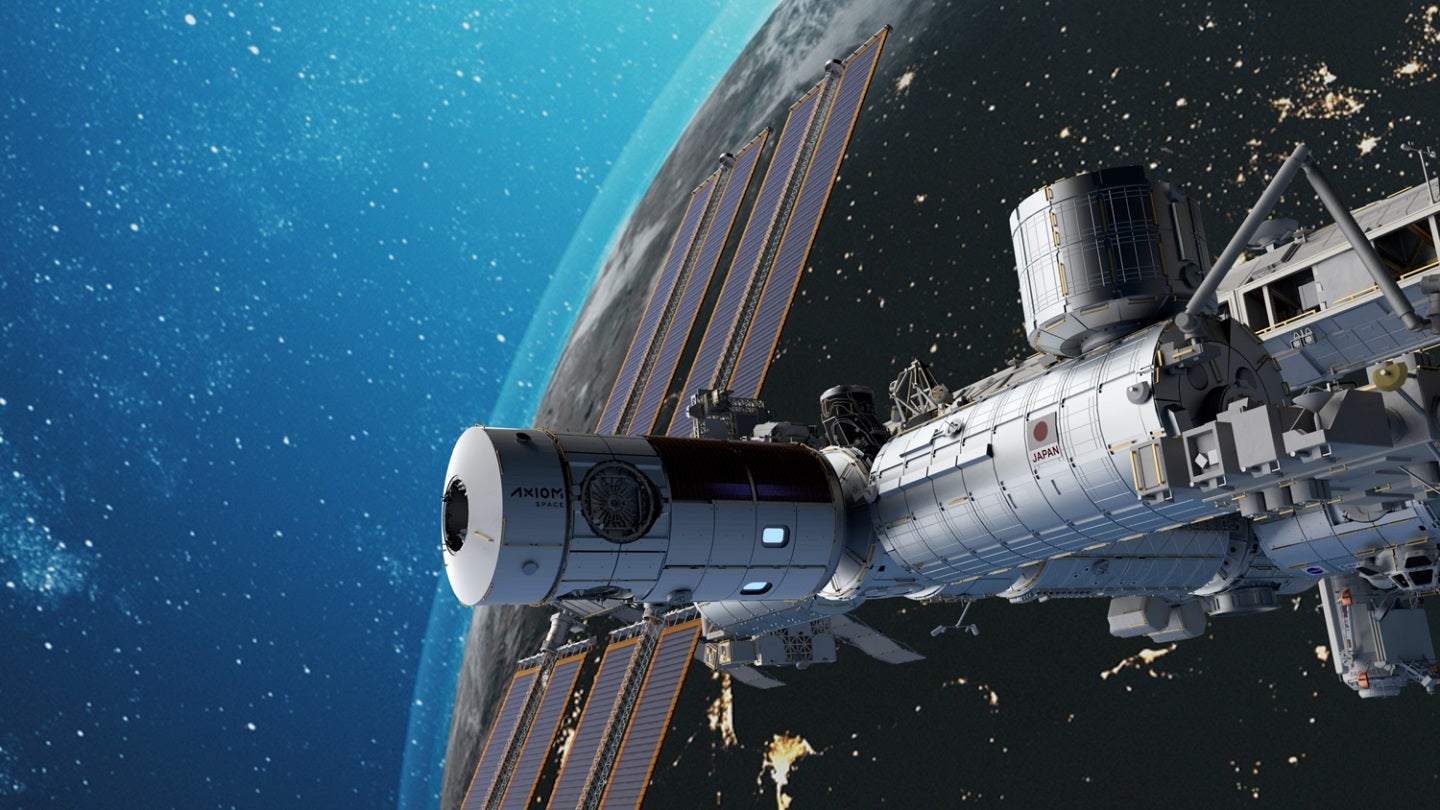
Cedars-Sinai has partnered with Axiom Space to test the feasibility of producing stem cells in space-based laboratories, to aid the development of the next generation of cell therapies.
Under the arrangement, materials and equipment required to manufacture stem cells will be delivered by Axiom Space to the International Space Station in the upcoming Ax-2 flight, which scheduled in early May.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
Mammal embryonic stem cells are harvested in the early stages of life and used for a variety of medical procedures, including cell-based therapies. However, because of the pull of gravity, it is challenging to manufacture them on a large scale on Earth.
Cedars-Sinai researchers will examine whether microgravity in space can make it easier to produce stem cells more efficiently.
The two-year mission is being funded by a $2m grant from space agency NASA.
In this trip, astronauts on the International Space Station will manufacture induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in space.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThese specialised iPSCs can be reprogrammed to return to a potent stage of “pluripotency” where they can transform into almost any tissue of the human body and subsequently be used to create customised remedies for crippling diseases.
The crew will also study whether microgravity has any effect on how the stem cells differentiate into different cell types, such as brain and heart cells.
Arun Sharma, a stem cell biologist is leading the laboratory affiliated with the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute, Smidt Heart Institute, and Department of Biomedical Sciences.
Co-principal investigator Arun Sharma said: “One of the major roadblocks in applying regenerative cell therapies on Earth is the lack of patient-specific cells capable of replacing damaged tissues and organs. “We are hoping to use the unique conditions of space to generate, expand and differentiate cells at a much larger scale than you can do on Earth.”







