The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the increasing need for secure collaboration and data sharing among organisations, stringent data protection regulations, and the growing adoption of cloud computing and distributed systems, as well as growing importance of technologies such as secure function evaluation, secure multi-party computation frameworks, and homomorphic encryption. These technologies enable secure computation across multiple parties, protecting sensitive information and fostering trust in collaborative environments. In the last three years alone, there have been over 3.6 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Cybersecurity: Secure multi-party computing. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
300+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 2.5 million patents, there are 300+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, byzantine fault tolerant blockchain, secure multi-party computing, and decentralised identity framework are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Secure hash algorithms (SHA), zero knowledge proof, and private blockchains are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are, firmware security, multimedia signal encryption, and biometric authentication, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
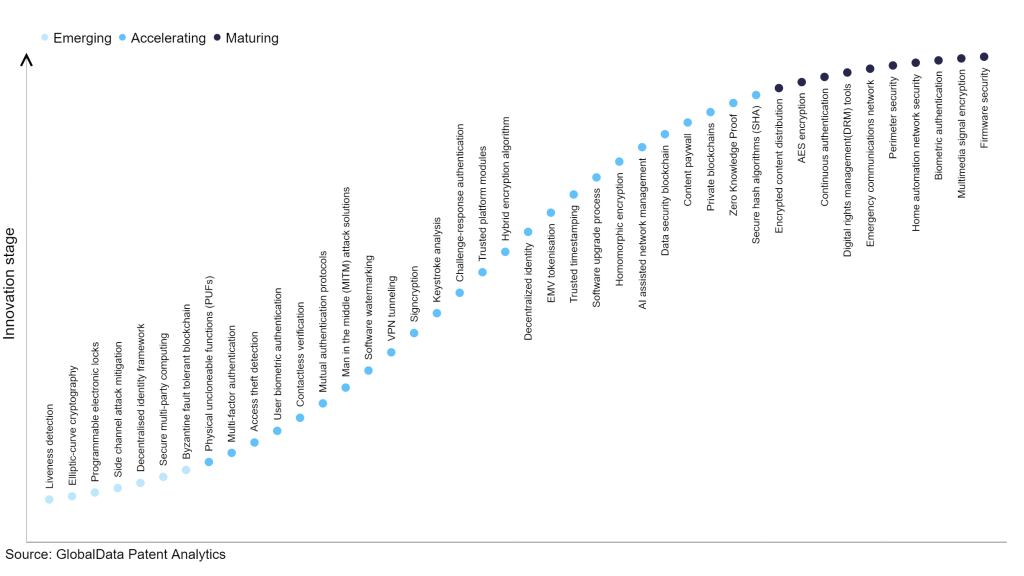
Secure multi-party computing is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Secure multi-party computing (SMPC) is an innovative cryptographic protocol enabling multiple parties to collaboratively compute a function while maintaining the privacy of their respective inputs. This approach ensures that the sensitive information held by each party remains undisclosed during the computation process. By employing SMPC, organisations can securely compute functions without compromising the confidentiality of their data, while ensuring the accuracy of the computed output.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 20+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of secure multi-party computing.
Key players in secure multi-party computing – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to secure multi-party computing
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone is a leading patent filer in secure multi-party computing. The company’s patents are aimed at invention for efficiently obtaining an aggregation rank while maintaining secrecy. An inverse substitution unit applies inverse substitution to the cross tabulation of a table. When the table is classified into groups on the basis of a key attribute, the last element of each group is aligned in order from the beginning and generates a vector share that represents an inverse-substituted cross tabulation.
A partial sum unit calculates a prefix sum from the inverse-substituted cross tabulation. A rank calculation unit generates a vector share from the result of the prefix sum that represents a rank in ascending order within a group.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include SoftBank Group and Visa.
By geographic reach, THOMSON LICENSING leads the pack, followed by nChain and Samsung Group. In terms of application diversity, TripleBlind holds the top position, followed by Magna International and Panasonic.
Cybersecurity innovation in secure multi-party computing has revolutionised the way multiple parties collaborate and process data while preserving privacy and security. This innovation allows multiple entities to jointly compute results without revealing their individual inputs, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity – Thematic Research.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







