The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks, regulatory compliance requirements, widespread adoption of cloud-based services, and growing importance of technologies such as biometric recognition systems, one-time password generators, smart cards, and mobile authentication apps to provide enhanced protection against unauthorised access and reduce the risk of data breaches and identity theft. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.5 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Cybersecurity in technology: multi-factor authentication. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
185+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 1.6 million patents, there are 185+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, homomorphic encryption and signcryption are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Zero knowledge proof, multi-factor authentication and secure hash algorithms (SHA) are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are DRM tools and AES encryption, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
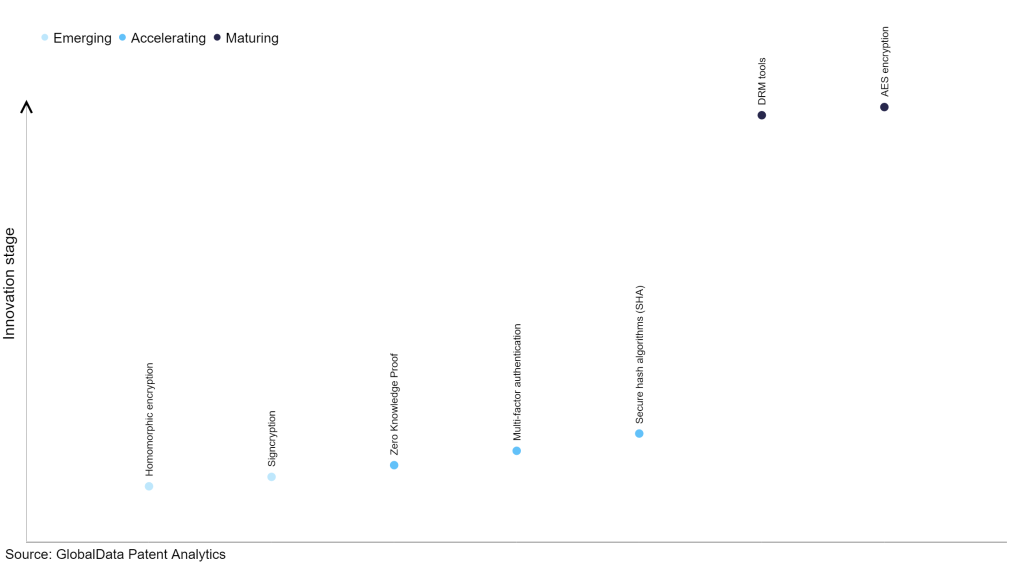
Multi-factor authentication is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Multi-factor authentication is a security procedure that mandates the use of two or more distinct credentials for system access. These credentials may involve knowledge/ possession/ inherence-based factors such as passwords, physical tokens, smartphones, or fingerprints, to ensure heightened protection against unauthorised entry while preserving the user experience.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 315+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of multi-factor authentication.
Key players in multi-factor authentication – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to multi-factor authentication
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Intel is one of the leading patent filers in multi-factor authentication. The company’s patents are aimed at invention describing an input device for a secure authentication protocol system receiving at least one user authentication factor in a pre-boot session. The input device can verify and store the received authentication factors. During a post-boot session, the input device may communicate the verified authentication factor and a stored post-boot session credential received during a prior post-boot session to an authentication engine executing in a trusted execution environment.
The authentication engine verifies if the received post-boot session credential is logically associated with an immediately preceding post-boot session. Upon successful verification of the received post-boot session credential, the verified authentication factors or data indicative of a successfully verified authentication factor received during the pre-boot session are used in the current post-boot session.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include Visa, MasterCard, Capital One Financial, and Headwater Research.
By geographic reach, Stream leads the pack, followed by Neology and Nio. In terms of application diversity, Digimarc holds the top position, followed by Early Warning Services and Nio.
Multi-factor authentication leverages advanced technologies and techniques to provide users multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or physical tokens. It enhances security by adding an extra layer of verification, making it more challenging for attackers to breach systems or impersonate users. By implementing robust multi-factor authentication solutions, organizations can mitigate the risks of identity theft, data breaches, and unauthorized access, bolstering cybersecurity measures and safeguarding sensitive information.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







