The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the need for stronger and more comprehensive cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber threats and attacks, and growing importance of technologies such as elliptic curves in mathematical cryptography, public key cryptography, digital signatures, and secure hash functions. In the last three years alone, there have been over 3.6 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Cybersecurity: Elliptic-curve cryptography. Buy the report here.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
300+ innovations will shape the technology industry
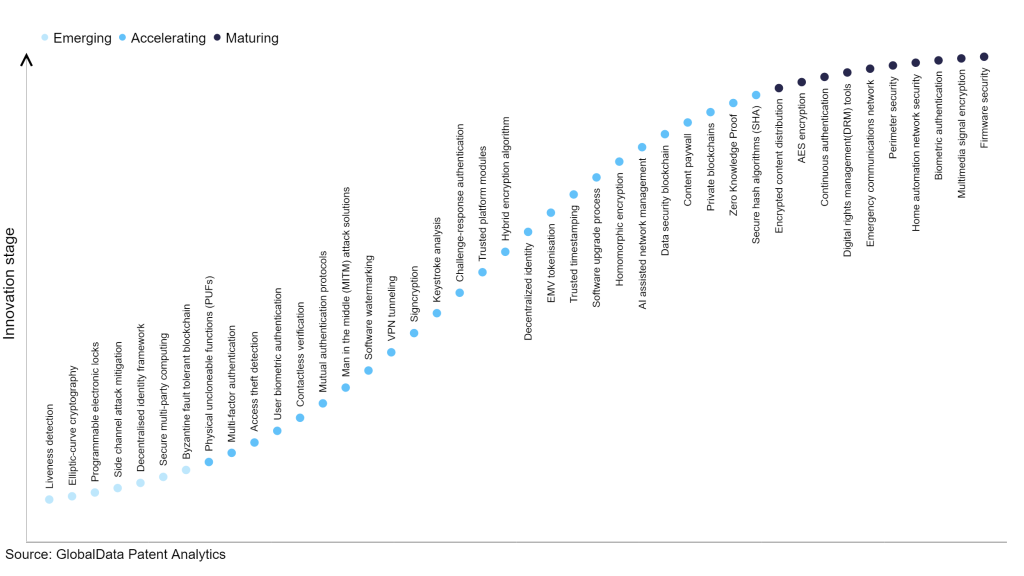
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 2.5 million patents, there are 300+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, byzantine fault tolerant blockchain, secure multi-party computing and decentralised identity framework are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Secure hash algorithms (SHA), zero knowledge proof, and private blockchains are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are firmware security and multimedia signal encryption, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
Elliptic-curve cryptography is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) is a cryptographic method that relies on the mathematical properties of elliptic curves over finite fields. It is a public-key encryption technique employed for digital signatures, key exchange, and other applications. ECC offers the advantage of using smaller keys while maintaining the same level of security as non-ECC cryptography. This feature makes ECC highly suitable for resource-constrained devices like mobile and embedded systems with limited memory and processing capabilities.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 20+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of elliptic-curve cryptography.
Key players in elliptic-curve cryptography – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
BlackBerry is a leading patent filer in elliptic-curve cryptography. The company’s patents are aimed at invention describing elliptic curve random number generation. An elliptic curve random number generator avoids escrow keys by choosing a point Q on the elliptic curve as verifiably random. An arbitrary string is chosen, and a hash of that string computed. The hash is then converted to a field element of the desired field. The field element regarded as the x-coordinate of a point Q on the elliptic curve and the x-coordinate is tested for validity on the desired elliptic curve. If valid, the x-coordinate is decompressed to the point Q, wherein the choice of which of the two points is also derived from the hash value.
Intentional use of escrow keys can provide for backup functionality. The relationship between P and Q is used as an escrow key and stored by for a security domain. The administrator logs the output of the generator to reconstruct the random number with the escrow key.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include nChain and Intel.
By geographic reach, nChain leads the pack, followed by Winbond Electronics and IBM. In terms of application diversity, nChain holds the top position, followed by Renesas Electronics and Mitsubishi Electric.
ECC helps in securing sensitive information, enabling secure communication, and protecting digital transactions across various domains. Its use of smaller key sizes offers enhanced security, faster computations, and reduced computational overhead, making it ideal for resource-constrained devices, thereby holding significant importance in modern cryptography.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity – Thematic Research.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







