The AI startup behind ChatGPT, OpenAI, has disrupted at least five online influence operations (IO) over the last three months as cybersecurity continues to face a skills gap.
In a blog post published yesterday (30 May), OpenAI stated that it had successfully disrupted online IOs from Russia, China, Iran and Israel.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
In many of the disrupted IOs, OpenAI stated that its ChatGPT tool had been used to generate online comments, long form articles and headlines that were used to spread misinformation and fuel online argument.
The IOs had primarily been fuelled by geopolitical tensions, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine and politics in the US and EU.
The disrupted Chinese IO, dubbed Spamouflage, had used OpenAI’s models to monitor and track social media activity across the Korean, English, Chinese and Japanese language. It tracked activity on sites such as X, Medium and Blogspot.
OpenAI stated that it had shared information about disrupted IOs with other industry insiders in an attempt to benefit the wider security research community.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataIn its 2024 thematic intelligence report into cybersecurity, research and analysis company GlobalData found that cybersecurity job vacancies had continued to rise into 2023 and 2024.
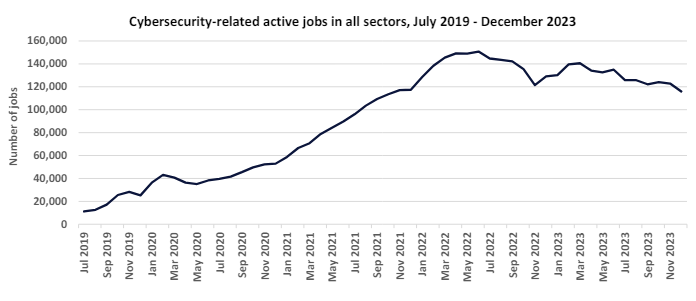
Demand for cybersecurity professionals has risen dramatically over the last two years, with job vacancies regularly over 100,000 a month since July 2021.
In 2023, the global cybersecurity workforce reached 5.5 million workers worldwide, but demand continued to outpace available staff.
Looking ahead, GlobalData forecasts that the rise of GenAI will continue to widen this gap.
By 2027, GlobalData estimates the total cybersecurity market will be worth over $290bn, achieving a CAGR of 13% from 2022.
Software is estimated to account for 44% of the total cybersecurity market by 2027, while services are expected to contribute around 37% of cybersecurity’s global revenues.







