
GlobalData believes that in 2022 and beyond, sustainability will be the most important theme discussed in corporate boardrooms and will continue to drive strategic and operational decisions for companies in all sectors and geographies. Despite the current economic and geopolitical climate, the pressure for companies to grow sustainably will not disappear.
Today, companies must react to pressure from a range of sustainable minded stakeholders to address issues like social inequality, corruption, tax avoidance, and climate change, head-on and in full public view. The financial sector is adding pressure for companies across all sectors to achieve net-zero, warning that climate risk is investment risk. Asset managers are voting against the management of companies that they feel are not adequately addressing sustainability issues, and governments are passing regulations to further drive green development. The European Union (EU) Green Deal, approved in 2020, is as a major regulatory milestone which aims to make the EU the first climate-neutral bloc by 2050 and promote development without increasing resource use. The EU plans to reach carbon neutrality by improving energy efficiency by over 32.5%, cutting greenhouse gas emissions by 55%, and boosting the share of renewable energy to above 32%. China aims to hit peak carbon dioxide emissions before 2030, achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 and increase the share of non-fossil fuels in primary energy consumption to around 25% in 2030.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the continued importance of sustainability. According to GlobalData’s 2021 ESG Global Management Insight Report, 67% of sustainability executives believe that the pandemic has acted as a catalyst for increased focus and action on sustainability issues.
For most organisations (63% according to GlobalData’s most recent survey findings), the environment is the primary focus of sustainability initiatives, with climate change the most pressing environmental challenge. Climate change is an existential issue. It is already having significant material impact on the global economy – disrupting many natural systems, accelerating wildfires, sea-level rise, coastal flooding, extreme storms, and human dislocation.
Huawei’s 2030 vision for green development
The most recent climate science from The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) is clear, global warming is expected to surpass 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels by 2040 with emissions in line with the agreement’s current pledges. According to the IPCC, there is ‘a brief and rapidly closing window of opportunity to secure a liveable and sustainable future for all’. Throughout this decade, urgent action is needed to transition the world to a low carbon and circular economy, and Huawei recognizes the pivotal role the business community will play securing a low carbon future.
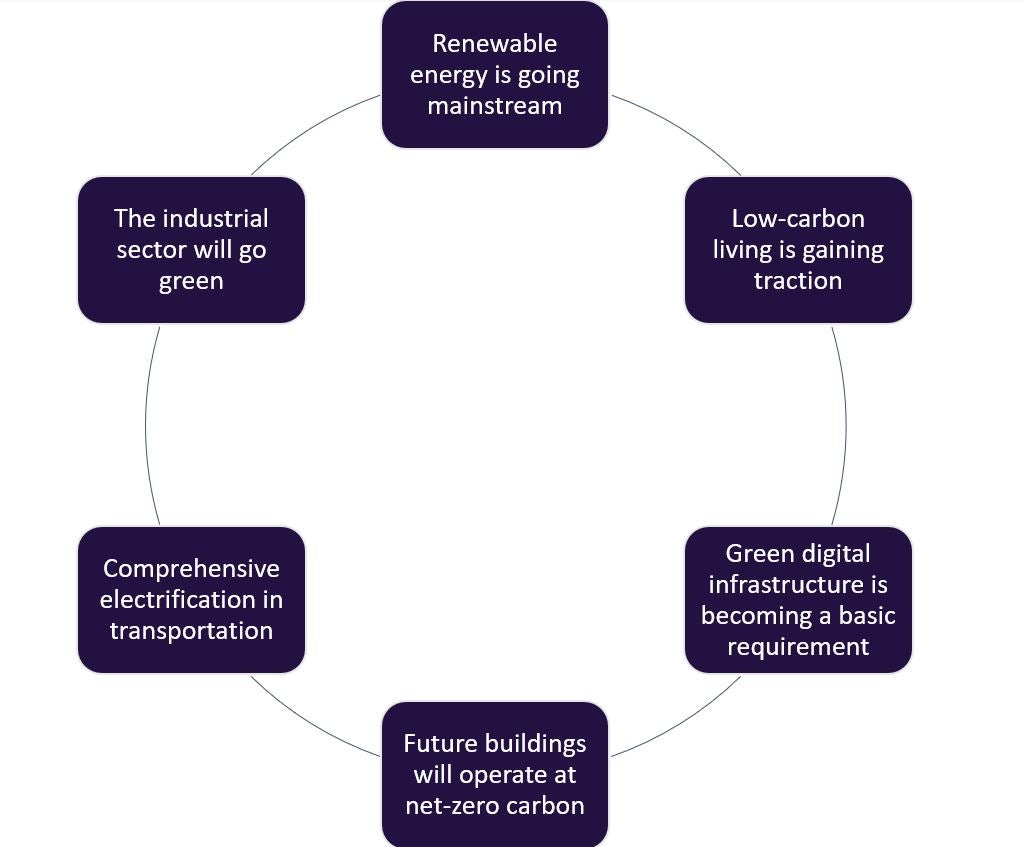
A new era of green development is emerging. The current wave of sustainability consciousness is unprecedented as the foundations are being laid for a low carbon future. The green development theme permeates Huawei’s entire ‘Intelligent World’ vision. This is very important to Huawei’s plan as it is central to the company’s aim of achieving the 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs). Huawei’s 2030 vision for green development is sixfold, underpinned by digital technologies like big data, cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) to establish lasting changes to the way we consume, live, and work:
How Green ICT supports green development
Our current levels of growth and consumption are placing considerable strain on the earth’s finite resources. To create a more sustainable future, we must decouple economic growth from environmental impacts and promote green development which does not come at the expense of the environment.
One may argue that accelerated digitalisation is counterproductive to green development. Technologies like cloud computing, blockchain, big data, artificial intelligence require considerable amounts of data center capacity and therefore emissions. However, Huawei’s position is that digitalization and decarbonization are two key drivers for green development. As the sophistication of digital technologies continues to develop, they will play an important role in supporting decarbonization initiatives as sensor data and industrial automation are combined with artificial intelligence to drive efficiencies and cut emissions.
Digitalization and decarbonization have a symbiotic relationship. As decarbonization demands continue to intensify, so this will push the pace of technological development in a more sustainable direction. In fact, Huawei predicts a 15% uplift in digital technologies across industries driven by decarbonization.
The ICT sector is stepping up to the plate
It’s important to recognize that all companies are on a journey when it comes to ESG. Some are further along than others, but all will require support along the way. The ICT sector has seized this opportunity, positioning products and services to help overcome the challenges companies in the highest emitting sectors face in addressing their ESG objectives, and Huawei is no exception in this regard.
Huawei will be relying on its core competencies: traditionally telecommunications and ICT services; and increasingly cloud computing, AI, and semiconductors, to firmly position itself as a leading provider of green services.
Huawei has identified three directions of green development from an industry perspective: energy efficiency of digital infrastructure, renewable energy development, and industry digitalization. The company believes these are key progress measures of green development.
Energy efficiency of digital infrastructure
Huawei predicts that by 2030, digital infrastructure will be 100 times more energy efficient. At first this seems like an ambitious target. However, when we consider the scale of investment by the ICT sector in improving the energy efficiency of data centers, networks, and operations, this ambition becomes more realistic.
Huawei is developing technologies to improve the energy efficiency of its data centers across multiple geographies by investing in extremely large antenna arrays (ELAAs), AI-enabled hibernation which improved efficiency by identifying when a network or individual component (e.g. server) is operating at a relatively low load or idle and switching that asset off or to a low power mode.
Renewable energy development
Huawei predicts that by 2030, more than 50% of all electricity globally will come from renewable energy. The push to transition to cleaner energy, driven by strong policies and financial support, will heavily impact the future of renewables. From 2024 onwards, renewables are projected to lead the energy mix, overtaking coal-fired power generation. Energy storage will play an increasingly important role in the global power sector as intermittent renewable sources such as solar and wind make up an increasing share of the mix.
Huawei breaks down this area into two sub areas: energy supply and energy consumption. Integrating digital technologies and power electronics will improve the power generation efficiency of solar photovoltaic (PV). Equipped with AI, PV plants will transform into intelligent systems which support autonomous operations. On the other hand, smart energy management and storage technologies will be used to build low-carbon buildings and campuses. Wide-bandgap semiconductor materials will help EVs achieve optimal energy efficiency and advancements in battery energy density will drive EV adoption.
Industry digitalization
Huawei projects that 50% of businesses will have adopted digital technologies by 2030. The highest emitting sectors are investing in digital technologies to execute net-zero strategies and help them to achieve their sustainability goals.
The industrial sector is being disrupted by various technologies across the entire value chain. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) allows companies to manage complex production processes in real-time with sensors that measure various parameters and affords them better supply chain visibility. Industrial companies can reduce resource consumption and predict future faults by using artificial intelligence to recognize patterns and make adjustments accordingly.
Even if we halt emissions today, we have created lasting damage to our environment. Therefore, we need to ramp up investment into carbon removal technologies such as carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS). These technologies are deployed to capture carbon dioxide before it reaches the atmosphere; it is then either purified for recycling or compressed into underground geological formations. While CCUS is still in its early stages, the technology has the potential to increase adoption by improving process visibility and by accurately measuring and monitoring the carbon captured and stored.
According to the SMARTer2030 report published by the Global Enabling Sustainability Initiative (GeSI), ICT has the potential to enable a 20% reduction of global carbon emissions by 2030 – 10 times the ICT industry’s own footprint.
Establishing a trusted partner is the way forward for green development
We have the knowledge, technical expertise, and collective will power at hand to be able to halve global emissions by 2030, we just need to deploy these solutions at scale. This is a significant challenge but is not unachievable. In line with the seventeenth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG), Huawei and GlobalData share the view that this challenge will demand cross-industry collaboration to drive the innovation required to transition to a low carbon economy. Establishing long-term partnerships with trusted companies is central achieving green development.


