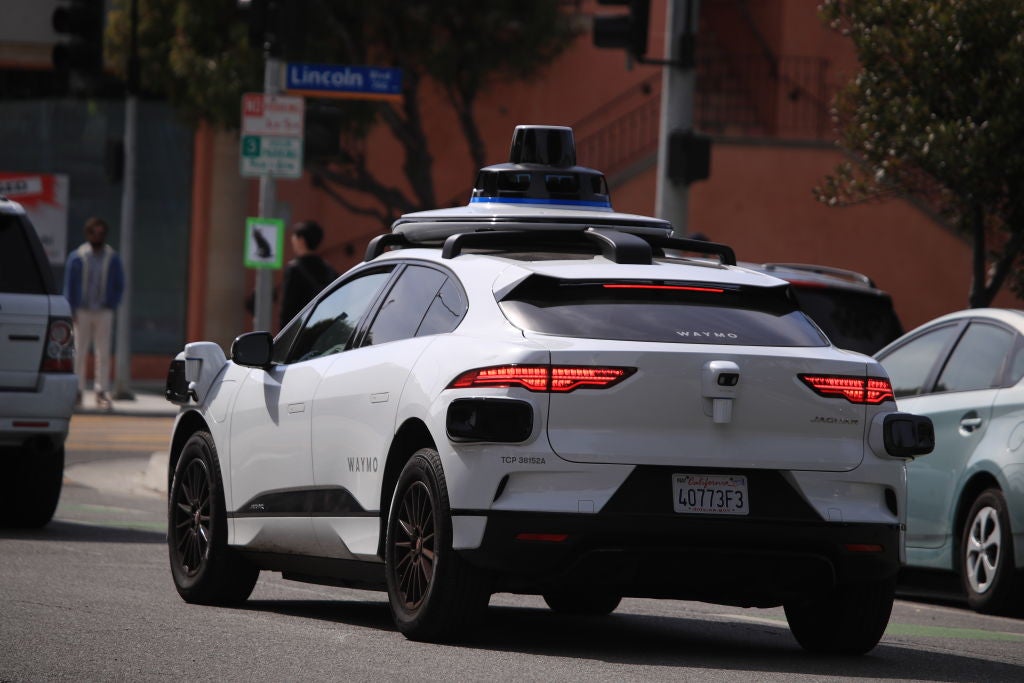
General Motors’s (GM) autonomous vehicle (AV) subsidiary, Cruise, has reportedly applied for permission to test its AVs across California state.
In June 2022, Cruise launched the first commercial, driverless taxi service (robotaxis) in a major US city after receiving a permit to operate in San Francisco – overcoming objections from city officials. Cruise is now looking to extend the area in which the company can legally operate commercial ride-hailing to include the entire state of California.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
According to the company, Cruise has registered more than a million miles of driverless travel with its fleet of 300 self driving vehicles, currently in service. The company is testing robotaxi services across various areas in the US including the cities of Phoenix and Austin.
Robotaxis are classified as having a level 4 autonomy, that is to say can be operated completely free from human oversight. A global race for widespread adoption of level 4 AVs is underway. GlobalData predicts China will lead in market penetration by 2036, followed by South Korea, Japan and North America.
US companies are ploughing billions of dollars of investment into driverless technology. GM is said to be investing around $2bn annually as part of CEO Mary Barra's pledge to double the company's revenue by 2030.
GM's investment in the robotaxi, transport-as-a-service (TaaS) business model for AVs, reflects similar investments by competitors including Google's AV subsidiary Waymo. Indeed, according to GlobalData thematic research: "TaaS is probably the single-most significant driver of demand for autonomous vehicles."
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataIn fact, many TaaS companies such as Uber aren’t expected to be meaningfully profitable until they can deploy self-driving robotaxis, according to the analyst.
Reasons for this include an AVs potential to both eliminate the cost of human drivers and operate for significantly longer hours. In addition, the high development cost of AVs is better absorbed by robotaxi fleet purchasers rather than private individuals. The cost to a private individual of a fully autonomous vehicle will be a barrier to market.







