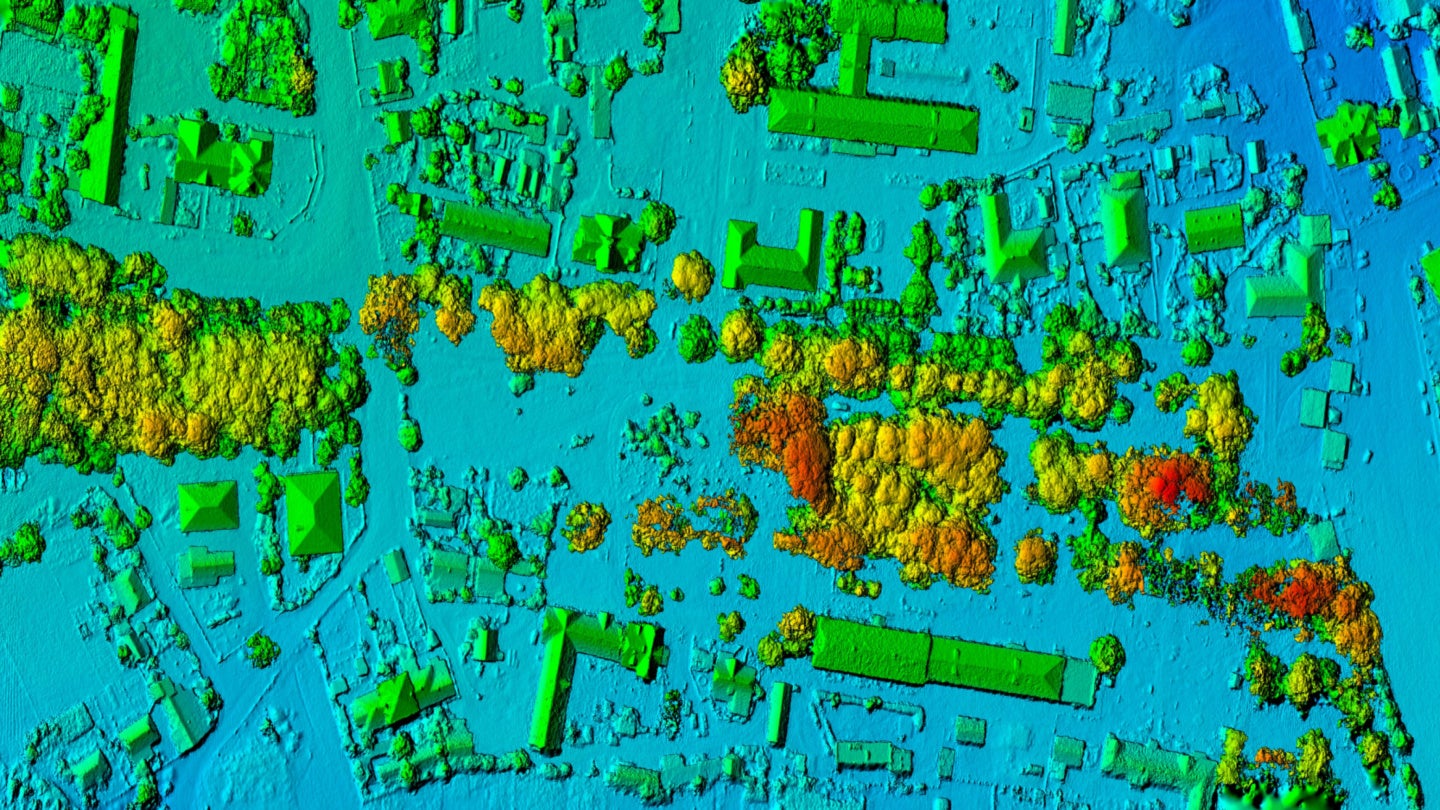
More companies are bringing to market geospatial tools as part of their machine learning portfolios, to find novel ways to tackle practical problems in many industries, including environmental services. AWS was the latest firm to do so, recently announcing the preview release of Amazon SageMaker‘s geospatial capabilities. The launch is significant, because it is the first time that the cloud computing giant offers customers the opportunity to make predictions using artificial intelligence applied to satellite and location data.
Geospatial data has many uses in industries including urban planning, retail, automotive, insurance, agriculture, and more. For example, maximizing harvesting of crops in agriculture, predicting car accident hotspots in urban development, combining maps with competitive intelligence to optimize store locations in retail, detecting old gas pipelines in utilities, etc.
Geospatial data is crucial to combating climate change
In sectors such as environmental services, applying AI to geospatial data helps companies analyze extreme weather events linked to climate change. It not only helps in real-time mitigation of the effects of such events, but also to forecast and help prevent their consequences before they happen. It is possible to obtain a wealth of information about natural disasters through the combination of AI and maps, for example. In the realm of insurance, geospatial data also makes it possible to assess and quantify the damage to property from flooding, tornadoes, and wildfires. These tools can facilitate the assessment of rising water levels, forecasting their future impact.
However, leveraging this type of data entails working with massive, unstructured data sets, from multiple sources and in different formats. The entire process, from data enrichment to visualization, can take months. As a result, data scientists sometimes spend a long time preparing and labelling the data, before even getting to write a single line of code.
Pre-built ML models simplify the process
AWS claims that SageMaker can accelerate and simplify the process of creating geospatial ML predictions by enabling customers to enrich their datasets, train geospatial models, and visualize the results in hours instead of months. To accelerate the task of building models for the most common uses, the company has incorporated built-in pre-trained deep neural network (DNN) models to its latest offering, and geospatial operators that help users access and prepare large geospatial datasets, alongside maps to visualize predictions. The process is automated to allow access to geospatial data sources from AWS (such as Amazon Location Service), open-source datasets (Amazon Open Data), or third-party providers (like Planet Labs).
For example, the Road Extraction visualization tool leverages satellite imagery to give users full visibility of what is happening on the ground, in the event of floodings or other emergencies, so that they can send directions to first-aid teams to identify which roads are safe. This can be combined with apps such as Foursquare to see the location of the nearest hospital within the area that is not flooded, directing medical staff and evacuating people out of the danger zone.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe market for geospatial tools and ML will continue to accelerate
The latest release of geospatial tools by AWS could be seen as a reaction to competitive pressure from the likes of Google Cloud, which dominates the market thanks in part to its conspicuous mapping tools.
However, other cloud providers including Oracle and especially Azure also offer compelling solutions. Microsoft has Azure Maps, a suite of geospatial services to incorporate location-based data into web and mobile solutions. Converting location data into knowledge is notoriously complex, and the providers that can offer tools for industry-specific use cases through simplified, automated processes will win the race.
The introduction of pre-built ML models will no doubt generate interest, and fast-growing industries such as environmental services will continue to benefit from these advancements.