The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by the growing need for privacy and confidentiality in digital transactions, regulatory requirements for data protection, and the increasing adoption of blockchain technology, as well as growing importance of technologies such as zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge (zk-SNARKs), zero-knowledge scalable transparent argument of knowledge (zk-STARKs), and other related mathematical algorithms. These technologies play a crucial role in enabling secure interactions, privacy-preserving identity verification, and confidential data sharing, shaping the future of cybersecurity in various domains. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.5 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Cybersecurity in technology: zero knowledge proof. Buy the report here.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
185+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 1.6 million patents, there are 185+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
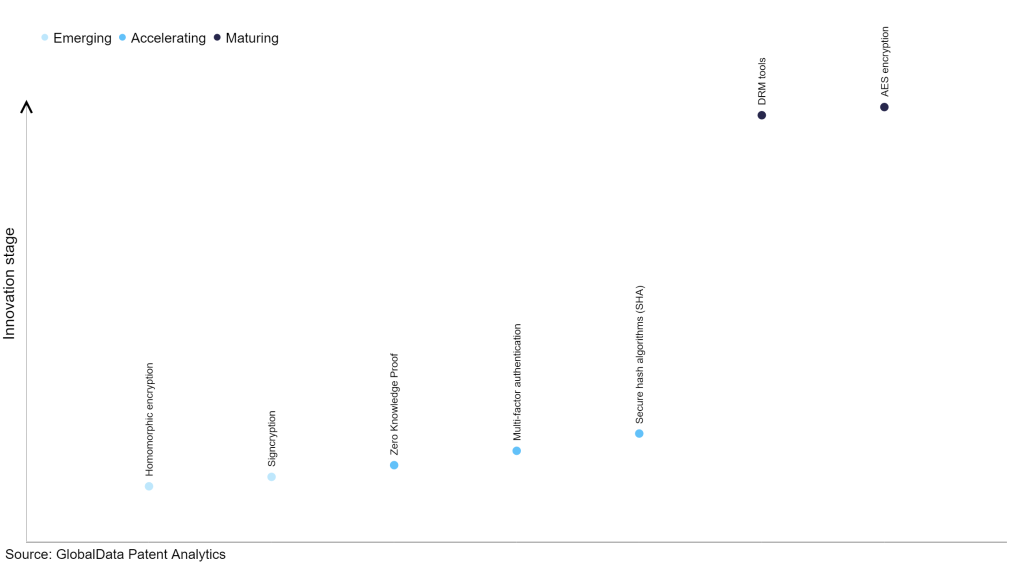
Within the emerging innovation stage, homomorphic encryption and signcryption, are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Zero knowledge proof, multi-factor authentication and secure hash algorithms (SHA) are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are DRM tools and AES encryption, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
Zero knowledge proof is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) is an innovative technique that allows for the verification of a statement's validity without disclosing any additional information. Using cryptographic methods, ZKP enables the demonstration of knowledge about a specific fact without revealing the actual content of that fact. For instance, in a ZKP protocol, two parties can prove their possession of an identical secret without disclosing the nature of the secret itself. This approach ensures privacy and confidentiality while still allowing for the establishment of trust and authentication in various scenarios.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 90+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of zero knowledge proof.
Key players in zero knowledge proof – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Alibaba Group is the leading patent filer in zero knowledge proof. One of the company's patents describes the primary database that synchronizes data values to a reading database within a specified time. In case of primary database failure, a transaction processing server quickly determines and processes transaction requests, acquiring transaction identification and data variation values. If the standby database does not contain the corresponding data value, an accurate data value is determined using the reading database and data variation value. The techniques described ensure uninterrupted transactions and enhance user experience.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include Intel and Advanced New Technologies.
By geographic reach, Intel leads the pack, followed by Journey.ai and Microsoft. In terms of application diversity, Intel holds the top position, followed by Alibaba Group and Advanced New Technologies.
Cybersecurity innovation in zero knowledge proof (ZKP) has emerged as a ground-breaking approach to securely authenticate and verify information without revealing sensitive data. ZKP allows a party to prove the authenticity of certain knowledge or claims without disclosing any specific details about that knowledge.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







