The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the increasing frequency and complexity of cyber threats, the need for robust security measures to protect against vulnerabilities, and the growing reliance on software in various industries, as well as growing importance of technologies such as secure coding, vulnerability scanning tools, encryption techniques, secure software delivery mechanisms, and automated security testing frameworks. These technologies aim to mitigate the risks associated with software upgrades, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data, protecting against malicious attacks, and maintaining the overall security posture of software systems. In the last three years alone, there have been over 3.6 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Cybersecurity: Software upgrade process. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
300+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 2.5 million patents, there are 300+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, byzantine fault tolerant blockchain, secure multi-party computing, and decentralised identity framework are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Secure hash algorithms (SHA), zero knowledge proof, and private blockchains are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are, firmware security, multimedia signal encryption, and biometric authentication, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
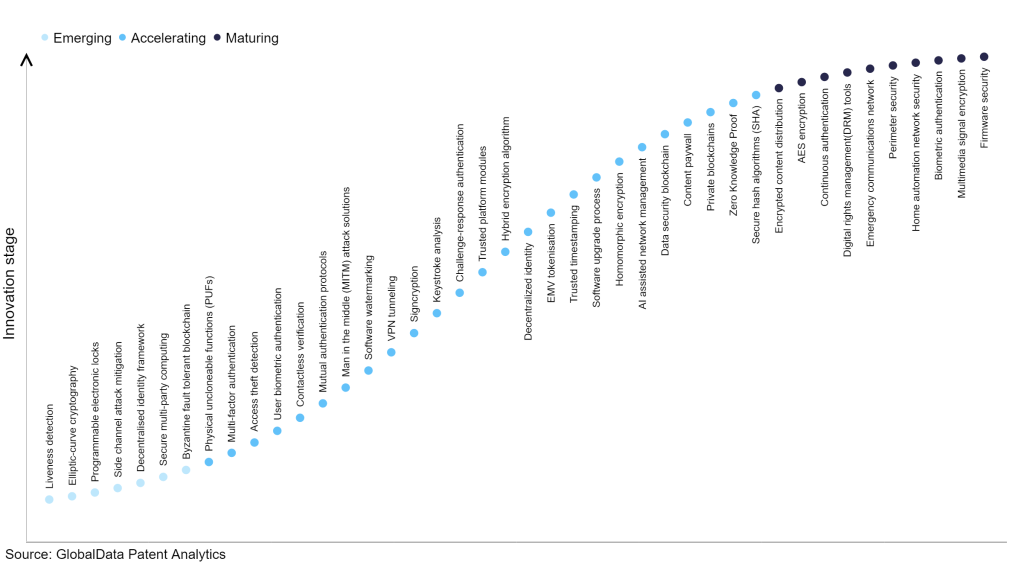
Software upgrade process is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
The software upgrade process refers to the procedure of enhancing software by incorporating new features, bug fixes, security patches, and various other improvements. Typically, this involves obtaining the most recent software version, installing it on the user's computer, and adhering to any accompanying instructions to ensure a successful and seamless upgrade. By going through this process, users can keep their software up to date with the latest enhancements, bug fixes, and security updates, ensuring optimal performance and an enhanced user experience.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 70+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of software upgrade process.
Key players in software upgrade process – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to software upgrade process
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Aurora Labs is one of the leading patent filers in software upgrade process. The company’s patents are aimed at invention related to identifying electronic control unit (ECU) anomalies in a vehicle. Operations may include monitoring the data representing real-time processing activity of the ECU, accessing the historical data relating to the processing activity and the expected processing activity of the ECU.
The real-time processing activity data is compared with the historical data, to identify at least one anomaly in the real-time processing activity of the ECU and a control action is implemented for the ECU when at least one anomaly is identified.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include International Business Machines (IBM) and Dell Technologies.
By geographic reach, Yanmar leads the pack, followed by THOMSON LICENSING and Synchronoss Technologies. In terms of application diversity, WS Audiology holds the top position, followed by Ford Motor and Juniper Networks.
Cybersecurity innovation in the software upgrade process focuses on enhancing the security aspects associated with updating software. Factors driving the growth of this market include the increasing frequency and complexity of cyber threats, the need for robust security measures to protect against vulnerabilities, and the growing reliance on software in various industries.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity – Thematic Research.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.






