The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by the increasing reliance on secure digital transactions, the rise in IoT devices, and the need for efficient encryption methods in resource-constrained environments, and growing importance of technologies such as exchange protocols, digital signatures, and secure communication channels. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.5 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Cybersecurity in technology: elliptic curve cryptography. Buy the report here.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
185+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 1.6 million patents, there are 185+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
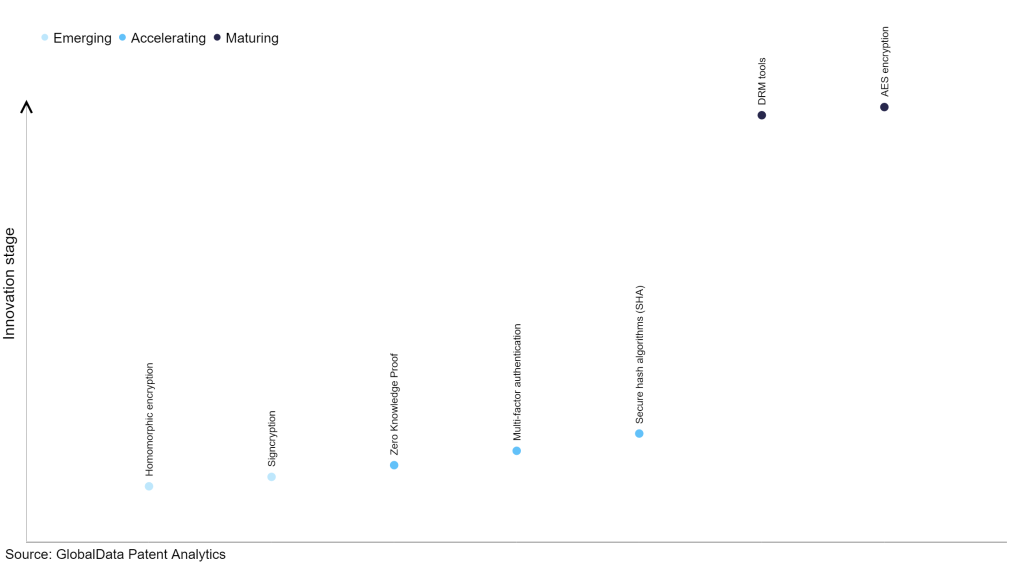
Within the emerging innovation stage, homomorphic encryption and signcryption are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Zero knowledge proof, multi-factor authentication and secure hash algorithms (SHA) are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are DRM tools and AES encryption, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
Elliptic curve cryptography is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) is a cryptographic technique founded on the principles of elliptic curves over finite fields. It is employed for ensuring secure communication, performing digital signatures, and facilitating key exchange. ECC offers an equivalent level of security compared to conventional encryption methods, but it achieves the same with smaller key sizes. The efficiency results in advantages in computation as well as bandwidth utilization.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 65+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of elliptic curve cryptography.
Key players in elliptic curve cryptography – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Among the companies innovating in elliptic curve cryptography, BlackBerry is one of the leading patents filers. The company’s patents are aimed at describing the process of executing the elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA), which involves performing arithmetic operations to determine a signature, some of which utilize a persistent cryptographic key. It is these arithmetic operations that can potentially expose ECDSA to a power analysis attack, enabling an attacker to ascertain the enduring cryptographic key. However, by altering the order of operations in the signature determination process and manipulating the inputs to these operations, power analysis attacks can no longer be effectively used to extract the long-term cryptographic key. Other prominent patent filers in the space include nChain and Intel.
In terms of application diversity, BlackBerry leads the pack, while Intel and NXP Semiconductors are in second and third positions, respectively. By means of geographic reach, nChain held the top position, followed by Texas Instruments and Qualcomm.
Elliptic curve cryptography can provide robust security in digital communications and transactions. ECC is known for its efficiency in terms of computational requirements and bandwidth usage, making it particularly valuable in resource-constrained environments. It offers the same level of security as traditional encryption algorithms, but with much smaller key sizes. This means ECC is crucial for securing data in various applications, including secure communication channels, digital signatures, and key exchanges.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







