The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by the amalgamation of technological progress, heightened connectivity, and the urgency for businesses to enhance efficiency and competitiveness in an ever-changing marketplace, and growing importance of technologies such as artificial neural networks, convolutional neural networks, and deep q-networks (DQNs). These technologies represent a subset of the tools and techniques used in deep reinforcement learning. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.5 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Artificial intelligence in technology: deep reinforcement learning. Buy the report here.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
185+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 1.6 million patents, there are 185+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
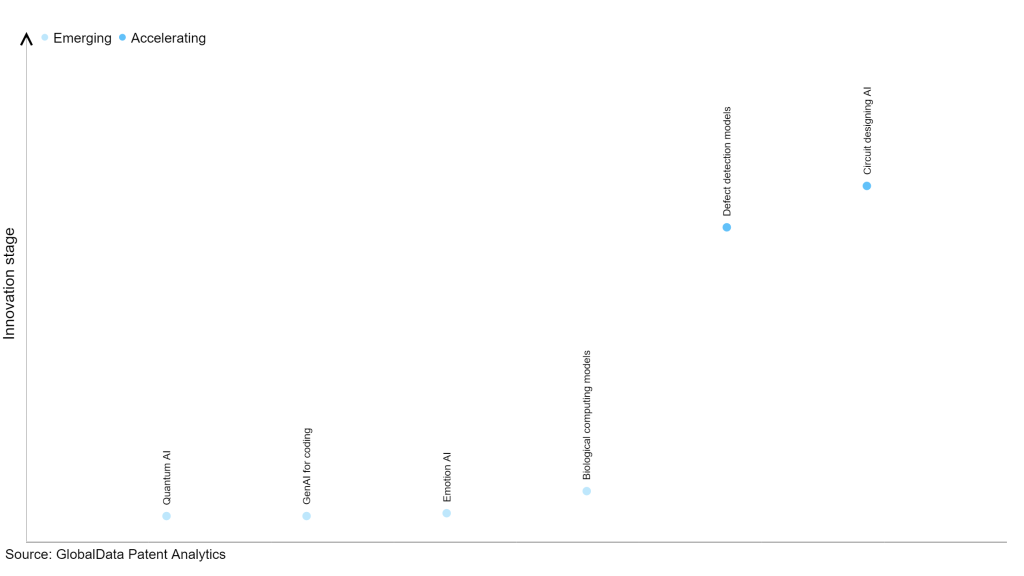
Within the emerging innovation stage, quantum AI, GenAI for coding and emotion AI are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Biological computing models, defect detection models, and circuit designing AI are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing.
Innovation S-curve for artificial intelligence in the technology industry
Deep reinforcement learning is a key innovation area in artificial intelligence
Deep reinforcement learning is a field within machine learning that merges reinforcement learning (RL) with deep learning techniques. It leverages deep neural networks to understand and process information from intricate input and output domains. Through deep reinforcement learning algorithms, agents can acquire sophisticated behaviours by directly learning from raw sensory inputs like images or videos. The ultimate objective of deep reinforcement learning is to develop autonomous agents that can effectively interact with their surroundings and optimise their actions based on the rewards they receive.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 365+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of deep reinforcement learning.
Key players in deep reinforcement learning – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
International Business Machines (IBM) and Royal Bank of Canada are among the leading patent filers in deep reinforcement learning. Other prominent patent filers in the space include Alphabet, Huawei, and Samsung Group.
By geographic reach, MediaTek leads the pack, followed by PlusAI and Sartorius. In terms of application diversity, Samsung Group holds the top position, followed by Huawei and Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson.
Deep reinforcement learning can handle high-dimensional data, learn complex behaviors, facilitate end-to-end learning, enable transferability and generalization, and drive advancements in various real-world applications, ultimately pushing the boundaries of AI research and development.
To further understand how artificial intelligence is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







