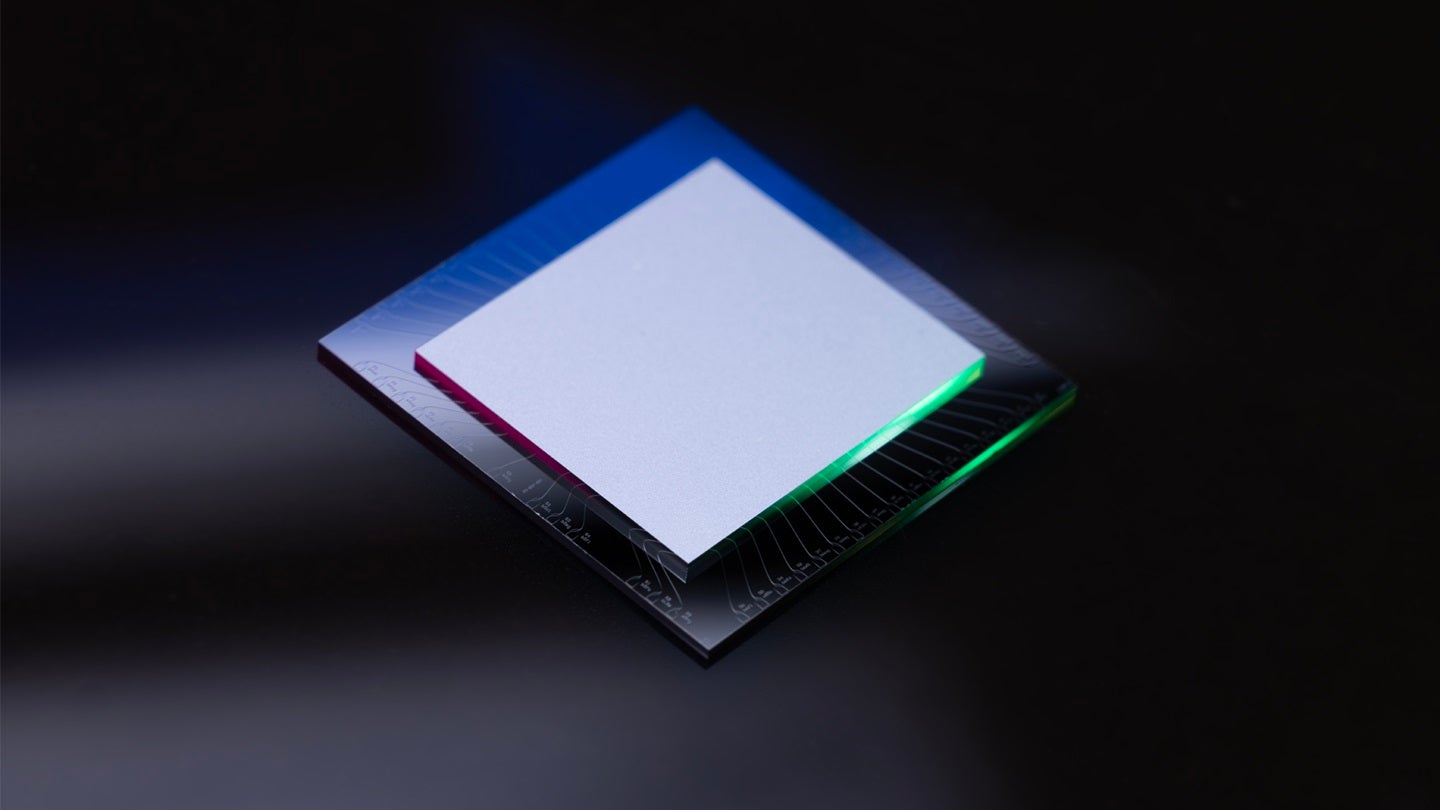
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has introduced Ocelot, a prototype quantum computing chip designed to reduce error correction costs.
The chip has been developed by the AWS Center for Quantum Computing at the California Institute of Technology.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
Ocelot is designed to slash the costs associated with quantum error correction by up to 90% compared to existing methods.
The new offering marks a step towards the creation of fault-tolerant quantum computers that can address complex problems beyond the scope of current conventional systems, the company said.
Ocelot is crafted to evaluate the efficiency of AWS’s quantum error correction architecture, AWS said.
The chip comprises two integrated silicon microchips, each about 1cm², arranged in a stacked configuration with electrical connectivity.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataSuperconducting materials on the microchips’ surface form the quantum circuit elements essential for operation.
The chip comprises 14 core components including five data qubits, known as cat qubits, five buffer circuits to stabilise the data qubits, and four additional qubits for error detection.
AWS said that cat qubits, named after the Schrödinger’s cat thought experiment, allows storage of quantum states for computation, supported by “high-quality” oscillators made from a superconducting material called Tantalum.
To enhance the oscillators’ performance, AWS material scientists have refined the processing of Tantalum.
AWS quantum hardware director Oskar Painter said: “With the recent advancements in quantum research, it is no longer a matter of if, but when practical, fault-tolerant quantum computers will be available for real-world applications. Ocelot is an important step on that journey.
“In the future, quantum chips built according to the Ocelot architecture could cost as little as one-fifth of current approaches, due to the drastically reduced number of resources required for error correction. Concretely, we believe this will accelerate our timeline to a practical quantum computer by up to five years.”
AWS’s design approach with Ocelot incorporates error correction from the outset, utilising cat qubit technology to inherently suppress certain errors and diminish the resources needed for quantum error correction.
This allows AWS researchers to merge cat qubit technology with other quantum error correction elements onto a microchip that can be produced at scale using conventional microelectronics industry techniques.
Recently, AWS said it plans to cease accepting new customers for its collaboration solution, Amazon Chime.
Amazon Chime service enables meetings, chats, and business all through a single application. The service is planned to be fully discontinued by 20 February 2026.







