The abundance of intricate, process-driven workflows in film and TV production demands both time and resources.
With rising costs and shrinking budgets, incumbents face tough decisions dedicating spending towards emerging technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI).
AI took the film and TV sector by storm in November 2022 following the release of ChatGPT, an AI chatbot that uses natural language processing (NLP) to facilitate human-like conversations. Thought leadership on potential use cases has forced incumbents to explore the potential of AI at every step of the film and TV value chain. It has also put a spotlight on the array of specialist AI vendors that have emerged in the sector over the last 10 years. These companies focus on using AI to increase the efficiency of specific processes such as filming, script analysis, casting, location scouting, budgeting, video editing, and visual effects.
But just how much of film and TV production can be automated using AI? Are specialist vendors the next step in unlocking cost-effective production?
TV pre-production
Pre-production is the planning stage of a film or TV project. It involves things like casting, location scouting, determining equipment needs, storyboarding, and budgeting. Several specialist vendors have emerged to help film and TV companies increase the efficiency of pre-production using AI.
The most well-known example is Cinelytic, an AI-based project management tool for the film and TV sector. Its platform allows users to vary parameters such as actors and budget and uses an AI algorithm to predict a film’s success. For example, users can choose actors based on historical data about past performance, audience appeal, box office potential, and global outreach. Other examples like Casting Droid and Superscout.ai are focused on specific aspects of pre-production like casting and location scouting, respectively.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData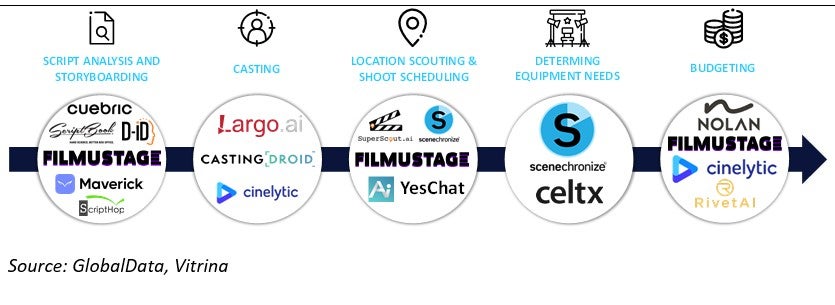
AI in production
The primary use case for AI in production is film cameras. High-end film cameras, used in major film and TV productions, have increasingly adopted AI as their sophistication has increased. For example, AI is inherently used in motion capture technology, which is a widespread and crucial tool for filmmaking, especially for animation. It uses computer vision algorithms and neural networks to enhance the process of capturing and interpreting human movement. Nowadays, virtually all film production cameras include motion capture capabilities. Film cameras also use AI to enhance features like auto-focus, image stabilisation, color grading, exposure control, and virtual cinematography.
Due to the pursuit of industry-best quality, specialist vendors have less presence in filming. However, some companies like MorphCast and Affectiva offer AI tools to analyse actors’ facial expressions and emotions during filming. Directors and editors can then use these insights to fine-tune performances.
AI is also being used for robotic camera systems to automate aspects of filming. An example here is Mark Roberts Motion Control (MRMC), which uses AI in its robotic camera systems to automate camera movements, allowing for precise and repeatable shots.
Post-production TV
Post-production is the final stage of film and TV audio production, where raw footage is processed into a finished product. Here, AI can assist with video and audio editing, visual effects, and localisation.
For instance, AI-enabled video editing software can analyse hours of footage, find the best camera angles, correct color-grading issues, and convert this into a coherent final shot in a matter of hours, something which would normally take an editing team several days.
Wonder Dynamics uses AI to create production tools to help filmmakers generate visual effects (VFX) and CGI elements. It only requires a single camera’s footage to catch an actor’s performance. It then transfers the footage to the CG character while ensuring automated animation, composition, and lighting in live-action scenes.
Furthermore, localisation, if done manually, would require extensive teams across several geographies to comb through hours of audio to first interpret the dialogue correctly and then hire voice actors to translate it into another language, but AI can do this much faster.
For example, Papercup uses its patented AI-powered translation platform to dub videos into other languages with realistic voices that display believable emotions. Specialist AI vendors offer a cost-effective way for film and TV companies to integrate AI.
To ensure production costs are kept low, incumbents must develop long-term partnerships with these companies, but with budget constraints, choosing which vendors to partner with remains a challenge. Incumbents must therefore also work to identify the pain points in their production processes to ensure each vendor partnership provides the highest value possible.









