The Odysseus moon lander experienced a navigational issue, which will cut the IM-1 mission short. Odysseus was launched on 15 February 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which charges $67m per launch. A lack of due diligence leading to the failure of its laser-guided ranger finders is believed to be responsible for the now-shortened mission. Despite this, the mission control centre still received imagery and data from the mission, meaning it was not a total failure. Missions in space are still very expensive, and even the smallest of errors can be catastrophic, which is why space is still seen as a risky investment.
Entering an era of space expeditions
Recent rushes to the moon are reminiscent of the space race of the 20th century. The space race has now become the space economy and has incredible potential for returns on investment. The vast unknown element can yield unexpected scientific, economic, or ecological findings that could potentially be very lucrative for the economy back on Earth.
The unforgiving environment of space exploration is matched only by the harsh financial reality of developing space technologies, which has made acquisitions of complementary companies, strategic suppliers, and partners more likely. The sector has become incredibly competitive, with various start-ups developing concepts for cost-effective rockets and satellites to rival the aerospace giants.
However, forays into space are risky. In August 2023, the Voyager 2 space probe stopped communicating when controllers sent the wrong command to the 46-year-old spacecraft and tilted its antenna away from Earth. Nasa’s Deep Space Network sent a new command hoping to repoint the antenna, using the highest-powered transmitter at Nasa’s huge radio dish antenna in Australia. The command took more than 18 hours to reach Voyager 2—which was more than 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometres) away—and another 18 hours to get a response. The risk paid off and the spacecraft continued returning data. However, this shows the fragility of space missions.
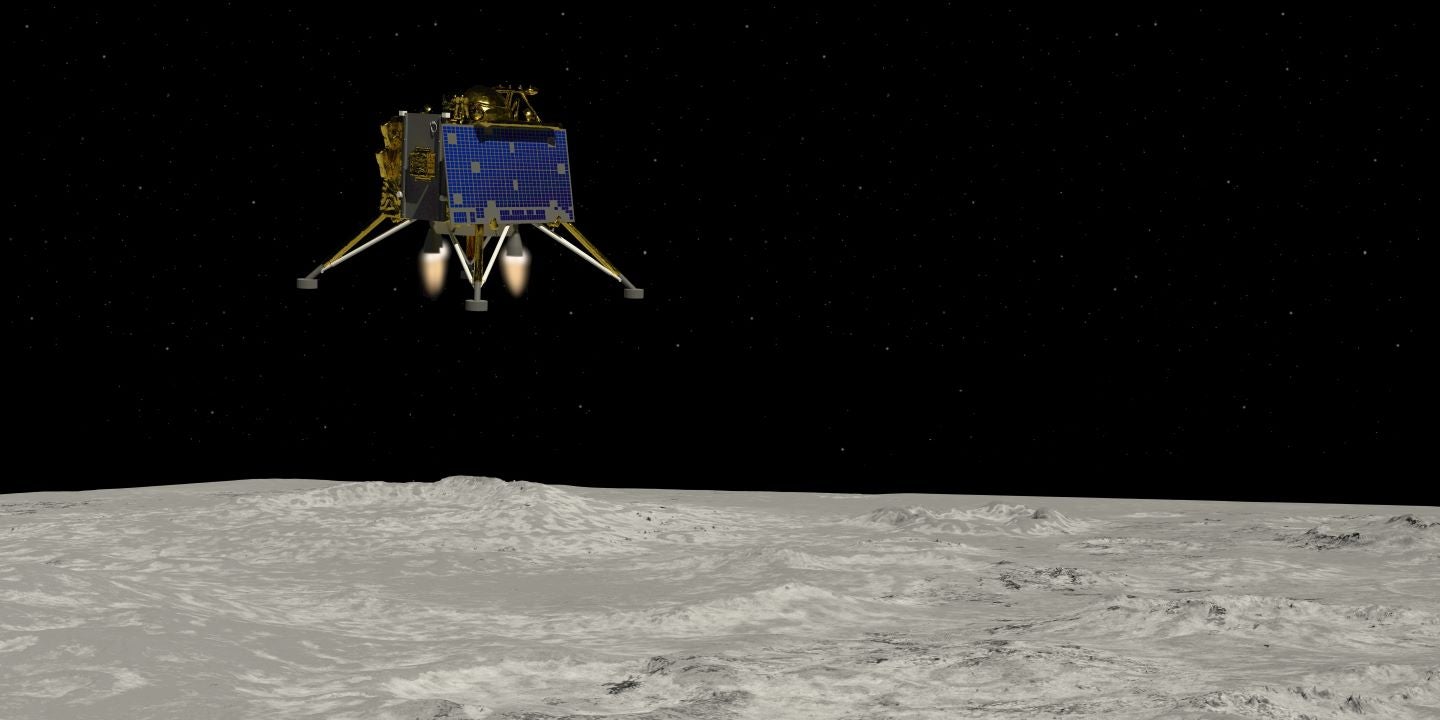
India’s and Russia’s fortunes in space are a blueprint for success and failure, respectively
India spent just $74m for its successful landing on the lunar south pole while Russia’s mission with a similar objective reportedly cost $200m. India’s launch infrastructure and space capabilities have been growing from strength to strength in recent years. This compares to Russia’s once world-leading space program, which has now faltered due to a lack of investment. The success and failure of the respective programs represent a microcosm of the direction that the programs are going in.
There are also obstacles affecting all space agencies. Recruitment is a barrier to growth for the space economy. Despite its vast size and potential, it struggles to compete for talent with sectors like technology and financial services. These sectors can offer better compensation to promising science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) graduates, leaving the space industry lacking talent. The successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 galvanised the youth in India and brought attention to the sector, which is increasingly being seen as an exciting and surprisingly viable career path. There is a lesson to be found in India’s recent success. The space economy is still in its early days, and failures will be commonplace. For missions, perfection is vital, and cutting corners with safety measures could prove fatal. However, these early failures may lead to important insights that make future missions safer and more likely to succeed. India’s mission encountered several failures before finding success and the team learned from these. For instance, the Chandrayaan-2 mission resulted in the Vikram lander crashing, due to a software error, whereas Chandrayaan-3 has been a success.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalData







Related Company Profiles
SpaceX
Indian Oil Corp Ltd