The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the increasing need for secure and transparent data management, regulatory compliance requirements, and the rising demand for trust and accountability in digital transactions, as well as growing importance of technologies such as cryptographic techniques, consensus algorithms, smart contracts, and permissioned network architectures to establish robust cybersecurity measures within private blockchains, protecting sensitive data, preventing unauthorised access, and enabling secure and efficient digital transactions. In the last three years alone, there have been over 3.6 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Cybersecurity: Private blockchains. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
300+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 2.5 million patents, there are 300+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, byzantine fault tolerant blockchain, secure multi-party computing, and decentralised identity framework are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Secure hash algorithms (SHA), zero knowledge proof, and private blockchains are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are firmware security, multimedia signal encryption, and biometric authentication, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cybersecurity in the technology industry
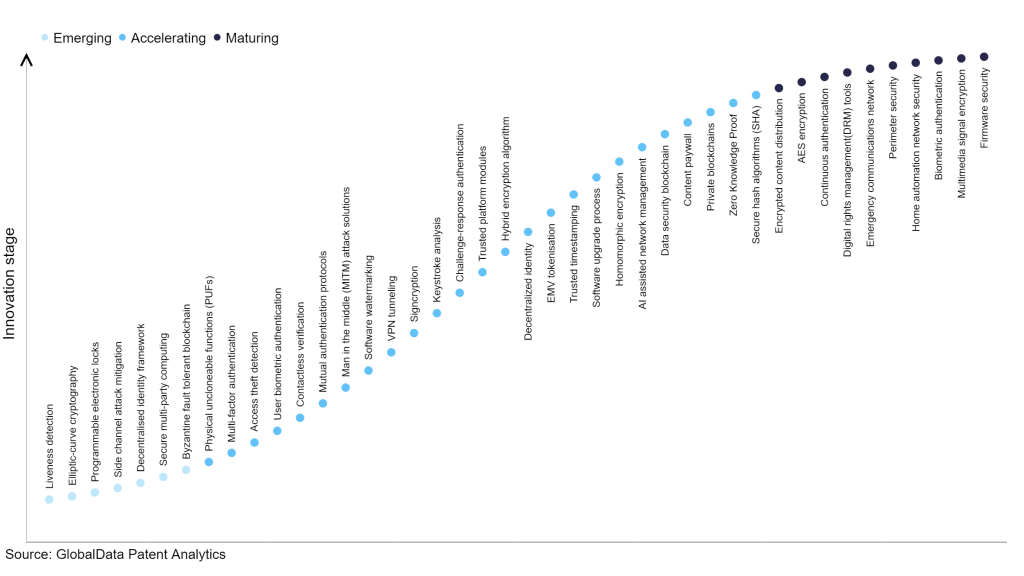
Private blockchains is a key innovation area in cybersecurity
Private blockchains are distributed networks governed by a single organisation, providing them with the ability to oversee and tailor the network according to their unique requirements. These blockchains serve as repositories for confidential data, facilitate the creation of digital tokens, and support the development of customised applications. In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains are not accessible to the general public, resulting in heightened security and efficiency.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 170+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of private blockchains.
Key players in private blockchains – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to private blockchains
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
SoftBank Group is one of the leading patent filers in private blockchains. The company’s patents are aimed at techniques of selecting consensus nodes in a blockchain. A voting process is performed by a plurality of shareholder nodes to generate a voting result for each shareholder node. The voting process comprises each shareholder node voting for a plurality of expected nodes, and the expected nodes and the plurality of shareholder nodes comprise a group of nodes associated with a blockchain.
A shareholder node is a node that owns at least one share. A voting result is verified for each shareholder node. After the voting process, several shares owned by each node of the group of nodes is determined based on the voting result. A plurality of consensus nodes is selected from shareholder nodes based on the number of shares owned by each of the shareholder nodes.
Other prominent patent filers in the space include nChain and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone.
By geographic reach, Kalypton leads the pack, followed by Shanghai Wangsu Science & Technology and Zeetta Networks. In terms of application diversity, First Datacorp holds the top position, followed by Bitmain Technologies and Ripple Labs.
Cybersecurity innovation in private blockchains can significantly enhance data security and privacy in various industries. Private blockchains are distributed ledger systems that restrict access to authorised participants, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity – Thematic Research.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







